Personal computer:
A small, single-user computer based on a microprocessor. In addition to the microprocessor, a personal computer has a keyboard for entering data, a monitor for displaying information, and a storage device for saving data.
Analog Computer:
A computer that represents numbers by some continuously variable physical quantity, whose variations mimic the properties of some system being modeled.
Microcomputer:
Your personal computer is a microcomputer.
Smartphones:Many cell phones can do a lot of things computers can do, including browsing the Internet and playing games. They are often called smartphones.
Wearable technology is a general term for a group of devices—including fitness trackers and smartwatches—that are designed to be worn throughout the day. These devices are often called wearables for short.
Many TVs now include applications—or apps—that let you access various types of online content. For example, you can stream video from the Internet directly onto your TV.
The Macintosh computer was introduced in 1984, and it was the first widely sold personal computer with a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey). All Macs are made by one company (Apple), and they almost always use the Mac OS X operating system.
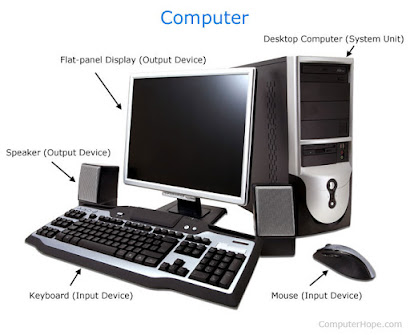
Monitor:
The monitor works with a video card, located inside the computer case, to display images and text on the screen. Most monitors have control buttons that allow you to change your monitor's display settings, and some monitors also have built-in speakers.
Newer monitors usually have LCD (liquid crystal display) or LED (light-emitting diode) displays. These can be made very thin, and they are often called flat-panel displays. Older monitors use CRT (cathode ray tube) displays. CRT monitors are much larger and heavier, and they take up more desk space.
Keyboard
The keyboard is one of the main ways to communicate with a computer. There are many different types of keyboards, but most are very similar and allow you to accomplish the same basic tasks.
Mouse:
The mouse is another important tool for communicating with computers. Commonly known as a pointing device, it lets you point to objects on the screen, click on them, and move them.There are two main mouse types: optical and mechanical. The optical mouse uses an electronic eye to detect movement and is easier to clean.
The mechanical mouse uses a rolling ball to detect movement and requires regular cleaning to work properly.
A trackball has a ball that can rotate freely. Instead of moving the device like a mouse, you can roll the ball with your thumb to move the pointer.
A touchpad—also called a trackpad—is a touch-sensitive pad that lets you control the pointer by making a drawing motion with your finger. Touchpads are common on laptop computers.
All general-purpose computers require the following hardware components:
Enables a computer to store, at least temporarily, data and programs.
Allows a computer to permanently retain large amounts of data. Common mass storage devices include solid state drives (SSDs) or disk drives and tape drives.
Central processing unit (CPU):
The heart of the computer, this is the component that actually executes instructions.


















Comments
Post a Comment