Hardware:
There are Three types of Hardware:
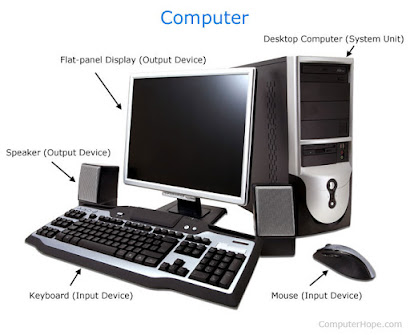
Input device:
Components which are used to input raw data are categorized under input devices. They aid in feeding data such as text, images, and audiovisual recordings. They even aid in file transfers between computers.
The keyboard is probably the most commonly used input device. Below are just some other types of input device.
Output device:
Hardware components that disseminate and display both data and information are classified under the output category.
Output is the culmination of a cycle which starts with the input of raw data and processing.
These components are sub-categorized under soft copy and hard copy output.
Soft copy output includes the intangible experience. The user derives visual satisfaction by reading a message through display components or listens to audio files through speakers.
On the other hand, hard copy output devices are tangible, like printouts of paper and 3D models.
Processing device:
Processing is the core function of a computer. It is the stage where raw data is transformed into information. Once data has been processed, it can be used for useful purposes.
Components that manipulate data into information are categorized under processing.
The microprocessor is the major device in this category. It works closely with primary memory during its operations. Data is stored temporarily in processor cache and primary memory during the processing period.
The microprocessor is subdivided into three important units, which work together in order to accomplish its function.
The units are:
The control unit: It manages and supervises the operations of the processor and other components that are crucial in data manipulation.
Arithmetic and logic unit: The ALU is responsible for all arithmetic and logic operations like addition, multiplication, subtraction, division, and comparison logic operations.
Register and cache: These are storage locations inside the processor that respond to the instructions of the control unit by moving relevant data around during processing.





Comments
Post a Comment